Understanding NIST SP-800-88r1 Methods: Clear, Purge, and Crypto Erasure
After almost a decade of engaging in conversations with IT Directors and high-level IT decision-makers at Fortune 2000 companies, it is apparent that everyone is data-sensitive, but few are data-educated. Data used to mean numbers and metrics used to make informed decisions, and that is still very true. However, it has now become a buzzword encompassing any digital footprint. Consequently, everything is now labeled as “data,” and the paranoia associated with its sanitization is, and should be, high. With that said, there is a very clear decision tree that can be followed to address these fears. NIST provides guidelines for all types of data, and understanding the different types of sanitization methods is paramount to ensuring companies’ peace of mind. In 2006, the NIST standard replaced the DoD 5220.22-M standard and has been recognized as the primary erasure pattern for government, military, and enterprises ever since.
ITAD Tech has been asked to handle a wide range of data-related tasks. Questions like, “Can ITAD perform a 10x wipe on my hard drives? Can you wipe our disks, shred them, and then incinerate them?” and, perhaps the most memorable, “Can you punch the drives with a drill and bury them somewhere?” have come up in our conversations. We can indeed perform a 10x wipe, but that would be extremely costly and excessive. We can also wipe, shred, and downstream for incineration, but again, these methods are overkill and come with a substantial price tag. No, we will not bury your hard drives (if you thought we would) because that would go against our certification status, multiple federal laws, and our zero landfill policy.
However, it’s crucial to understand that these questions stem from fear and anxiety rather than methodical guidelines. If a company or entity is more concerned about the sanitation of their data than our government and military, then that company should establish its own internal processes for data sanitization to ensure that the media never leaves organizational control.
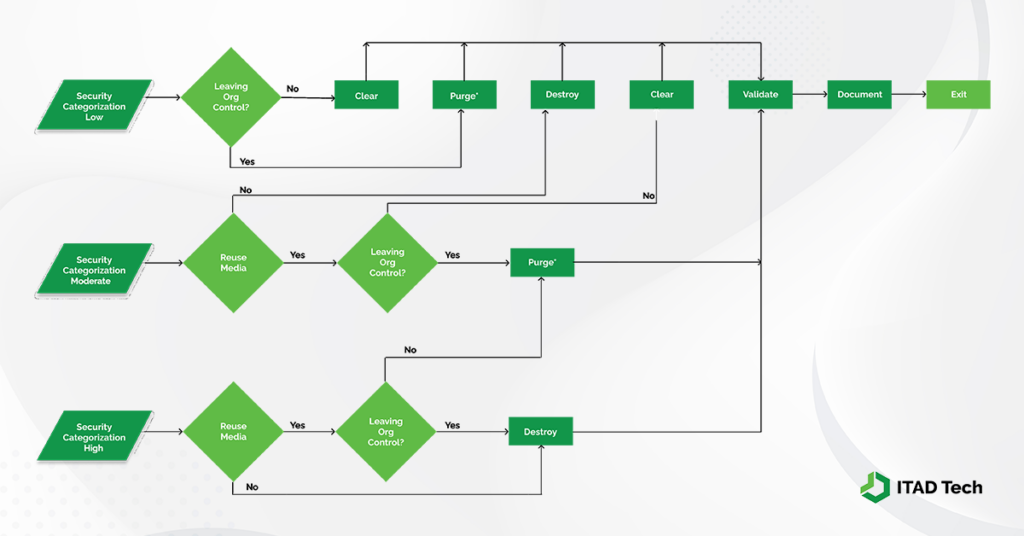
In today’s digital age, data security and privacy have become paramount concerns. Properly disposing of sensitive information is essential to protect individuals and organizations from data breaches and unauthorized access. The National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) has provided guidelines in Special Publication 800-88 Revision 1 (SP-800-88r1) for media sanitization, offering various methods for data erasure. In this blog post, we will explore the differences between three of these methods: Clear, Purge, and Crypto Erasure, and when to use each one. ITAD Tech has created its own graphic below, modeling the NIST publication decision tree. The original can be found here.
-
Clear Method
The Clear method, as outlined in NIST SP-800-88r1, is the least secure method of media sanitization. It involves overwriting data with a single pass of random characters or a fixed pattern, making the original data less accessible but still potentially recoverable with advanced tools and techniques. This method is suitable for situations where the confidentiality of the data is not a critical concern, such as when repurposing media within the same organization or disposing of non-sensitive data.
When to Use Clear:
- When the data is not sensitive and there are no legal or compliance requirements for secure data erasure.
- When you plan to reuse the media within your organization.
- In situations where speed and efficiency are more important than maximum security.
- Purge Method
The Purge method, also known as Secure Erase, is a more secure data erasure technique compared to Clear. It involves using built-in hardware or software mechanisms to overwrite all user-accessible storage locations on a device with a series of random or fixed data patterns. This process is highly effective in rendering the original data practically unrecoverable, even with sophisticated recovery methods. Purge is suitable for securely erasing media containing sensitive information, especially in compliance with various data protection regulations.
When to Use Purge:
- When you need to securely erase media that contains sensitive or confidential data.
- To comply with legal or regulatory requirements for data erasure.
- Before repurposing or disposing of media that may be used by others outside your organization.
- Crypto Erasure Method
The Crypto Erasure method is the most secure option outlined in NIST SP-800-88r1. It involves not only erasing the cryptographic keys used to protect data but also securely erasing the associated data itself. By destroying the keys, it ensures that even if someone gains access to the storage media, they cannot decrypt the data. Crypto Erasure is suitable for highly sensitive data and critical systems where the risk of unauthorized access must be minimized. It is important to remember, crypto erasure methods are only available in newer media with encryption. Most SSD are eligible but can vary by disk manufacturer.
When to Use Crypto Erasure:
- When dealing with extremely sensitive data, such as classified information, trade secrets, or personal identifiable information (PII).
- In scenarios where there is a high risk of media falling into the wrong hands.
- When strict security measures are required to comply with industry-specific regulations or government standards.
Choosing the right method for media sanitization, whether Clear, Purge, or Crypto Erasure, depends on the sensitivity of the data and the level of security required. It’s crucial to assess your organization’s data protection needs and comply with relevant legal and regulatory requirements when determining the appropriate method. While Clear may suffice for non-sensitive data, Purge and Crypto Erasure should be the preferred choices for securing confidential information and maintaining data integrity. By following NIST SP-800-88r1 guidelines, you can ensure that your data is disposed of properly and reduce the risk of data breaches and privacy violations. Our Director of Compliance here at ITAD Tech can also be made available for a one-on-one consultation to assist in verifying, auditing, or creating your organization’s best practices. Click here to schedule.